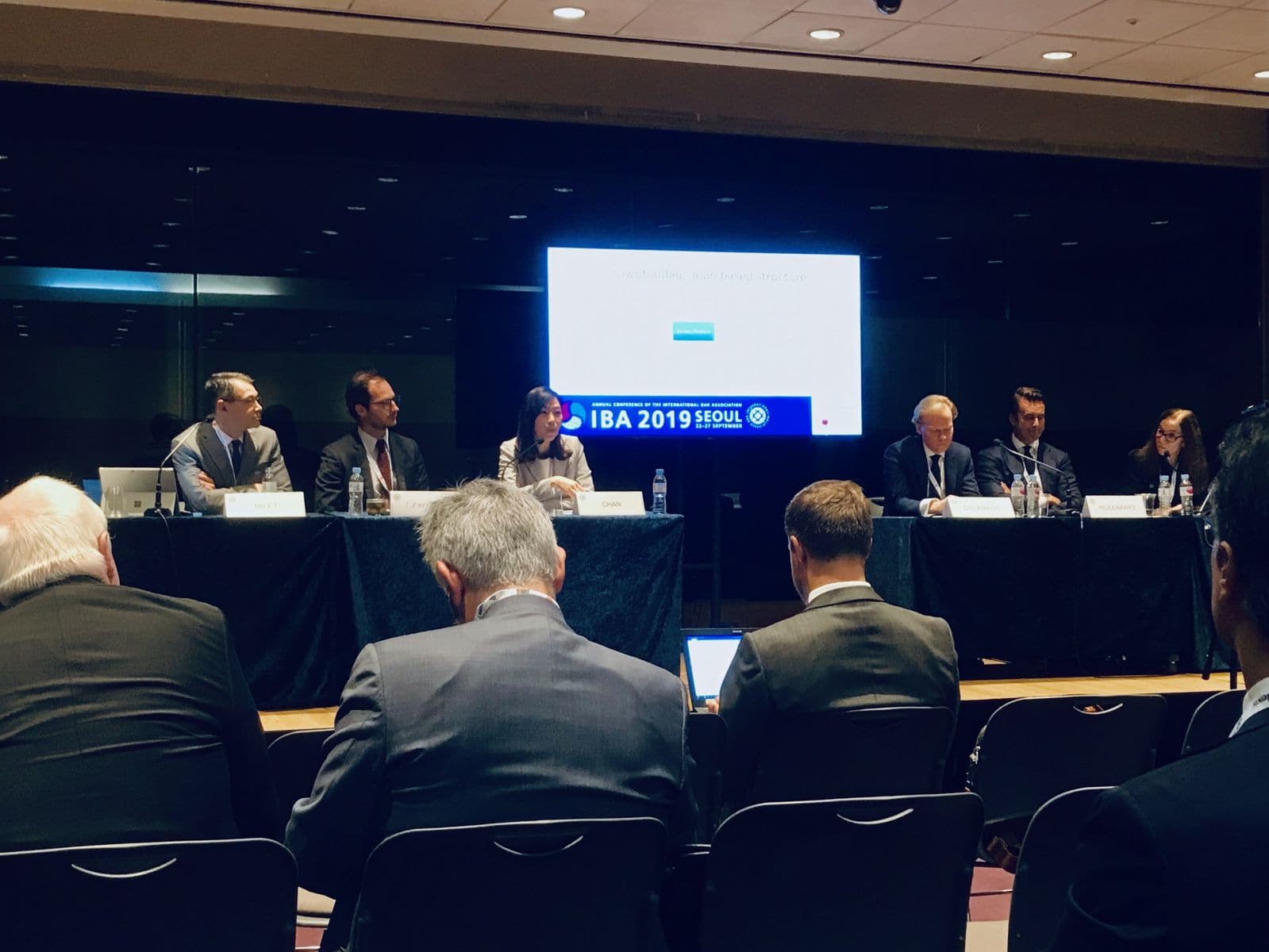
The International Bar Association (IBA) Annual Conference is the premier conference for legal professionals worldwide to meet, share knowledge, network, build contacts and develop business. It also serves to advance the development of law and its role in business and society and to learn from the experience of others. This year, the conference had been held at the COEX Convention & Exhibition Center in Seoul on the 22-27 September 2019.
Anna Chan, Head of the Tax Advisory, Partner, has been invited to be the panelist speaker on the topic “Shadow Banking and its tax implication”. The session was well attended with over 50 officers and delegates all of whom are themselves tax experts of their home jurisdictions. Issues such as availability of tax incentives, risk of transparent entities, withholding tax on interest, interplay of DTA have been covered. Amongst the speakers, we have leading tax experts from the Netherlands, US, Canada, Germany and Luxembourg. The presentation has received lots of positive feedback.

 Suite 503, 5/F, St. George's Building, 2 Ice House Street, Central, Hong Kong
Suite 503, 5/F, St. George's Building, 2 Ice House Street, Central, Hong Kong +852 2868 0696
+852 2868 0696