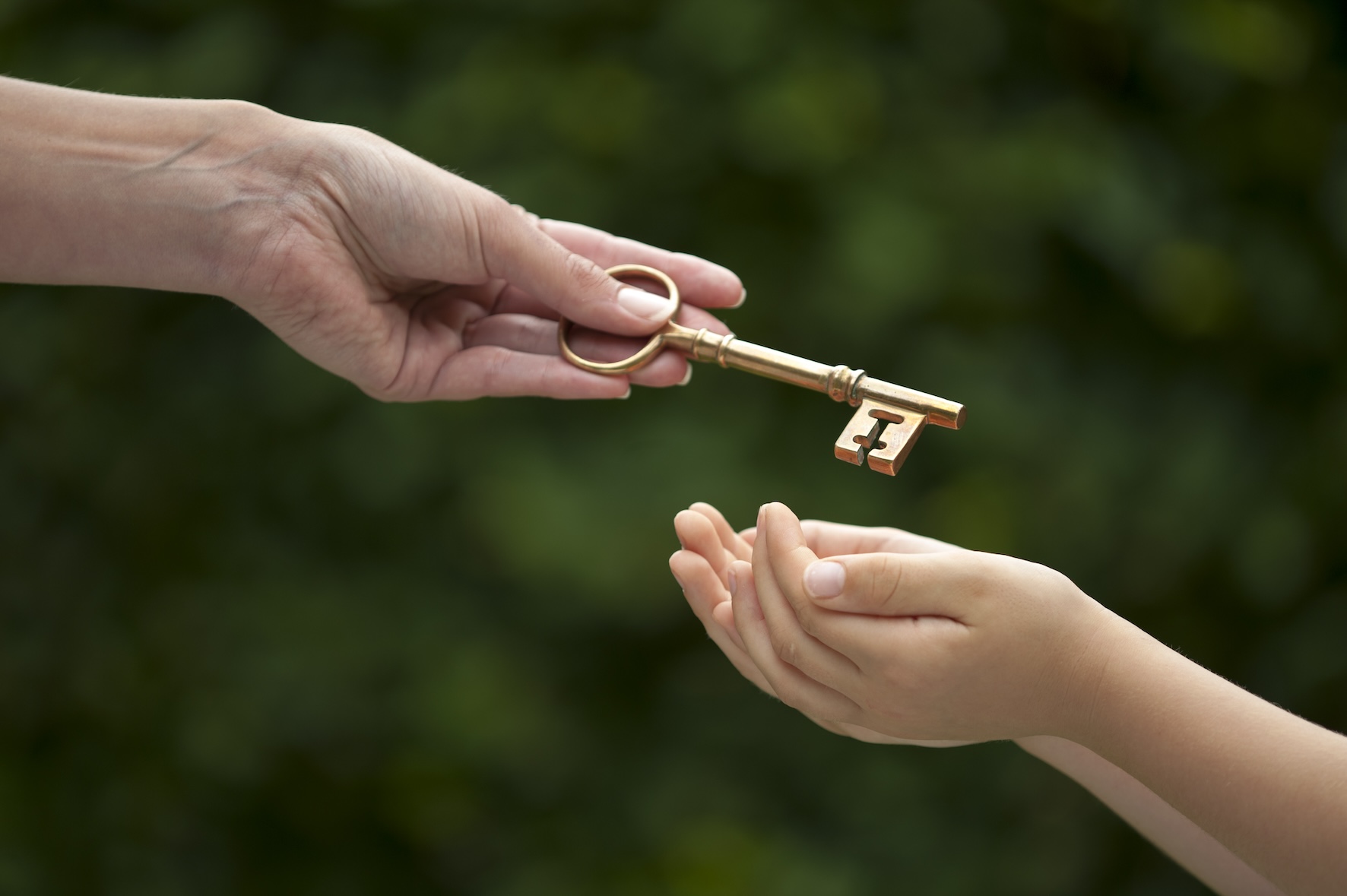
Over the years we have been asked by friends and clients alike a question along the lines of, “How do I persuade/bribe/force my children to take over my business?” Some have been more diplomatic in their phrasing but this has been a common desire of many a business owner. The hard work of building a solid, thriving enterprise may have taken place over many decades, yet none of the children are interested in taking it over. What to do? One volunteer is worth five pressed men so the exercise of free will rules but here are some options (not comprehensive) that can be considered:
1. When succession planning time arrives, accept with gratitude that businesses come and go as a fact of life and consider selling the business. “Getting all your ducks in a row” means bringing business records up-to-date, ensuring key personnel are on board and doing everything to ensure the business can be sold at the highest price possible. It would be a shame to have the price beaten down because of intellectual property issues, expired licences or key staff being difficult, for example. Make sure your business is in order and make it as attractive as possible! Do not simply close down the business without enjoying some final gains, whether it be through asset and/or share sale(s). Distribute the proceeds as desired and enjoy a well-deserved, around-the-world vacation as the beginning of the rest of your life.
2. For those with at least one child interested or potentially interested in taking an active part in the business, create a primary family trust that holds the family’s business shares and assets. The terms of the trust can be creatively devised, with two examples below:
2a) Create sub-trusts for each child, with children willing to run the family business holding more shares or assets in their sub-trusts. Sub -trusts can vary in terms of their voting rights, distributions and entitlements. Incentives can be also be written into the trust terms. For example, actively contributing children can enjoy accelerated vesting and/or greater shares if and as they meet certain milestones with the business. Non actively contributing children would still receive shares but with slower vesting schedules; or
2b) Family members actively working in the business could receive market rate remuneration including bonuses commensurate with their job duties separate and apart from their sub-trust allocations. The sub-trusts could then be equally allocated amongst the family members. Consider giving super voting rights to those actively engaged in the business.
The family trust could have rigid governance terms or more flexible governance whereby a trustee or family council could consider distribution events regularly or on a case-by-case basis. Governance that is flexible allows for evolving circumstances and needs, including varying degrees to which second and third generations are able to maintain amicable and working relationships.
Family trusts are structures that can be tailored to fit unique circumstances. For example, some family members may be prudent in their finances while others have less control over their spending patterns. A well devised family trust can optimise the preservation of wealth for each family member.
In short, you cannot force your children to commit to your heart’s desire but you can certainly incentivise and treat them fairly when it comes to extending the life of your family business. Probably the most important consideration of all is to maintain harmony within the family or at least attempt to diminish the chances of discord, by planning ahead with proper professional guidance.
Disclaimer: This article is for reference only. Nothing herein shall be construed as legal advice, whether generally or for any specific person. Oldham, Li & Nie shall not be held liable for any loss and/or damage incurred by any person acting as a result of the materials contained in this article.
 Suite 503, 5/F, St. George's Building, 2 Ice House Street, Central, Hong Kong
Suite 503, 5/F, St. George's Building, 2 Ice House Street, Central, Hong Kong +852 2868 0696
+852 2868 0696