New Trend of Japanese Corporates Retreating from China
28 Apr 2020
In early April 2020, the Japanese Government announced its plan to earmark about USD$2.2 billion as part of its economic stimulus package to help manufacturers to shift their production out of China. This effort has surfaced following the outbreak of coronavirus in China and its devastating disruptions to supply chains after temporary suspension of production bases in various parts of the country.
According to latest statistics, there are over 30,000 Japanese entities having establishments and presence in the PRC. Not surprisingly, most of them structure their investment in China via Hong Kong intermediaries for tax efficiency reasons. With the rolling out of the stimulus measures, will we be witnessing a new trend of Japanese companies moving out from China? What are the factors the enterprises should consider on their decision to “exit” China? What is the most tax efficient way to structure the investment post-exit? Should the Japanese enterprises maintain their regional head office in Hong Kong post-exit?
To leave or not to leave?
Targeting at Japanese manufacturers whose production is highly dependent on China (including pharmaceutical products, automobile, electronic components and other computer components), this new funding aims to encourage these manufacturers to build a stronger supply chain by shifting more high-value added productions back to Japan (Total: JPY 220 billion) and diversifying other manufacturing activities to neighbouring ASEAN countries (Total: JPY23.5 billion yen). Depending on the company size, these subsidies will cover from at least one half (for large corporations) to two-third (for SMEs) and even 75% (for SME groups) of their relocation expenses, including building and equipment acquisition and installation.
Though the proposed domestic return may gain support from export-oriented companies due to the rising labour costs in China and the US-China Trade War while some others may consider strengthening their procurement chain from outside China, there might be hesitation for enterprises with strong domestic market demand in China (notably the automobile industry). In addition, it is expected that the Mainland authorities, with a very strong desire to attract foreign enterprises to develop its high-technology (e.g. AI and 5G), will continue to provide more incentives to convince them to stay in China. At present, the tax incentives to such sector include a 15% preferential Corporate Income Tax (“CIT”) rate designated to foreign enterprises which are qualified as new/high technology enterprises, key software enterprises, technology-advanced service providers and those operating in Qianhai Shenzhen-HK Modern Services Industry Cooperation Zone and Zhuhai Hengqin New Area. Besides, tax reductions and exemptions also apply to specific industries and projects. For instance, qualified new/high-tech enterprises (established in certain parts of PRC) and software enterprises are entitled to enjoy a “2+3” tax holiday, meaning that they could enjoy first two years of exemption from CIT followed by three years of 50% CIT reduction.
Costs of exiting China – How to shut down a WFOE?
However attractive the stimulus measures might be, if the costs outweigh the benefit one could potentially receive, Japanese enterprises might still have hesitation to exit China. Currently, there are a number of ways to shut down a wholly foreign-invested enterprise (or commonly called “WFOE”) in China, with the most common being a formal dissolution. After paying up all the salaries and social insurances, taxes and debts, the WFOE must submit dissolution applications with various Chinese authorities one by one (including Commerce Bureau, Industrial and Commercial Administration Bureau, Statistic Bureau, Finance Bureau, Tax Bureau, State Administration of Foreign Exchange, etc.). The entire process, though complicated and time-consuming (often take around one year), remains the prudent way for management and shareholders as non-compliance by simply walking away and abandoning the WFOE may result in severe repercussions (including penalty, criminal and personal liability and failure to establish a new business in China again). The likely costs involved shall include administrative and other dissolution expenses, publication of notice and tax clearance prior to dissolution. Investors should therefore be mindful and seek independent advice for the best course of action before terminating their operation in China.
Whether to Keep Hong Kong Regional Head Office
Historically, Hong Kong is preferred over Singapore as a better option for Japanese enterprises to expand their business, likely because of the vibrant capital market, the more volatile stock market, an independent judiciary and a simple and competitive tax system. More importantly, Hong Kong’s strategic location in the post-CEPA regime allows Japanese investors to have access to the opportunities in Mainland market.
As alternative to the manufacturing bases in China, Japanese enterprises have found vigour by establishing more than 10,000 bases (2019) in other Southeast Asian countries, such as Thailand (3,925 bases, representing 5.2%), Indonesia (1,911, 2.5%), Vietnam (1,816, 2.4%), the Philippines (1,502, 2.0%) and Malaysia (1,295, 1.7%). Despite the similarity between the tax system in Hong Kong and Singapore, in determining whether Hong Kong or Singapore is more appropriate to set up their regional head office, enterprises should also consider the following factors:-
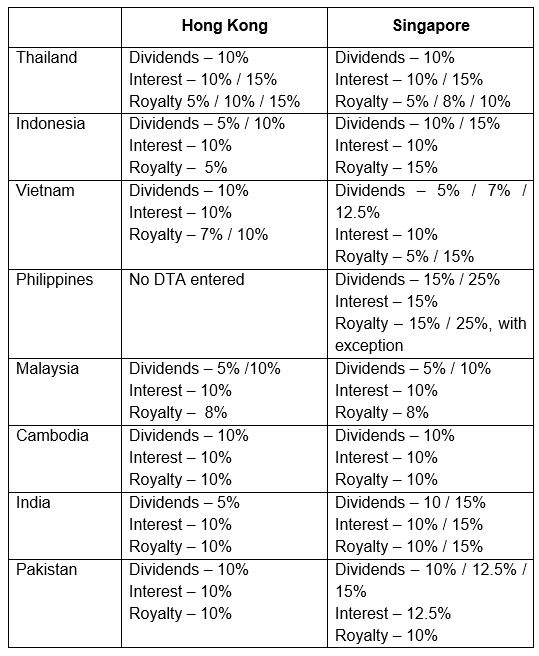
- The relevant Double Taxation Agreements (“DTAs”) that HK and Singapore have each signed with these ASEAN countries — While business profits are not generally at issue because they are taxed in the country where they are derived (and not in Hong Kong or Singapore on the basis of territorial source concept), attention should be paid to the reduction of withholding tax levied on incomes (e.g., dividends, interest and royalty) to be received by the Hong Kong or Singaporean head office. The relevant applicable withholding tax rates under the DTAs with the eight ASEAN countries are summarised in the table below.
Financing Needs and Future Investors’ Pitching — Hong Kong remains the market leader in equity and debt capital raisings in Asia possessing US$2.4 trillion worth of bank assets (triple of its keen competitor Singapore). With strong physical and technological infrastructure, Hong Kong has edge over Singapore to meet corporate financing needs with a domestic market capitalisation of US$4 trillion (as compared to US$0.8 trillion in Singapore) and its corporate bond issuance stands at US$33 million (more than double of Singapore). Coupled with Hong Kong’s proximity to their underlying businesses in Japan, better access to strong equity and debt capital raising markets in Hong Kong will continue to attract Japanese corporations seeking a stronger presence or expansion in the region.
- While two cities appear to be on par in terms of various tax incentives, regard must be made to other non-tax factors, e.g. availability of talent pool, corporate structure, etc.
If you have any question regarding the topic discussed above, please contact our partner Ms. Anna Chan at anna.chan@oln-law.com for further assistance.
Disclaimer: This article is for reference only. Nothing herein shall be construed as Hong Kong legal advice or any legal advice for that matter to any person. Oldham, Li & Nie shall not be held liable for any loss and/or damage incurred by any person acting as a result of the materials contained in this article.
 Suite 503, 5/F, St. George's Building, 2 Ice House Street, Central, Hong Kong
Suite 503, 5/F, St. George's Building, 2 Ice House Street, Central, Hong Kong +852 2868 0696
+852 2868 0696